Please refer to Introduction to Accounting Class 11 Accountancy Exam Questions provided below. These questions and answers for Class 11 Accountancy have been designed based on the past trend of questions and important topics in your class 11 Accountancy books. You should go through all Class 11 Accountancy Important Questions provided by our teachers which will help you to get more marks in upcoming exams.
Class 11 Accountancy Exam Questions Introduction to Accounting
Class 11 Accountancy er Science students should read and understand the important questions and answers provided below for Introduction to Accounting which will help them to understand all important and difficult topics.
Meaning & Definition of Accounting
Accounting is an information system which receives data inputs, process the same and give its output in the form of information which is useful for decision making. Accounting is also called the language of business.
Father of Accounting: Luca Pacioli (Italian Mathematician)
American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) defines “accounting is an art of recording, classifying and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money,transactions and events which are in part, at least, of a financial character and interpreting results thereof.”
Thus, accounting is the art of recording, classifying, summarizing, analyzing and interpreting the financial transactions and communicating the results to the interested persons.
Some relevant aspects of the above definition:
1. Economic events – It means the business transactions. It may be external or internal:
a. External event – Transfer of something of value between two or more entities.
Examples: Payment of wages to employees, Purchase of goods from a supplier, Sale of goods to a customer, Receipt of income by way of commission etc.
b. Internal event – It is an economic event takes place within the organization.
Examples: Issue of raw materials from stores to production department, Supply of stationery items to the office, Return of raw materials from production department to stores etc.
2. Identification, measurement, recording and communication
a. Identification – It involves the identification of events that are to be recorded in the books. It implies observing and selecting the events that may be recorded.
b. Measurement – Transactions that can be measured in terms of money are only
recorded. Eg., Sale of goods, Purchase of goods, Purchase of Machinery etc.
c. Recording – After identification and measurement of economic events, they are recorded in a chronological order.
d. Communication – After the above three stages, the accounting information has to be communicated in a proper form to the management or other users in the form of reports like profit and loss account, balance sheet etc.
3. Organisation – It means an entity that stands for performing business activities either for profit or for not-for-profit. It can be a sole proprietorship, partnership, co-operative society, company, Municipal Corporation or any other association of persons.
4. Interested users of Accounting Information – Many users need financial information for decision making purposes. These users can be divided into two categories:
a. Internal Users: It includes Chief Executive, Financial Officer, Vice President,
Business Unit Managers, Plant Managers, Store Managers, Line Supervisors, etc.
b. External Users: It may include, the present and potential investors (shareholders),Creditors (Banks and other Financial Institutions, Debenture holders and other lenders), Tax Authorities, Regulatory Agencies (Department of Company Affairs,Registrar of Companies, Securities Exchange Board of India), Labour Unions, Trade Associations, Stock Exchanges, Customers etc
Types of accounting information / Branches of Accounting / Accounting Disciplines
1. Financial Accounting – It is the original form of accounting, which is used to find out the results of operations (success or failure) and to provide information about the financial position (soundness or weakness) of the business. It is relates to the past period and is expressed in monetary terms.
2. Management Accounting – It is concerned with accounting information that is useful to management for decision making. Unlike financial accounting, which produces annual reports mainly for external users, management accounting generates weekly or monthly reports for an organisation’s internal users such as departmental managers, chief executive officers etc. It may include the reports of available cash, monthly sales,amount of orders in hand, state of accounts payable and receivables, stock of raw materials etc.
3. Cost Accounting – It is the process of accounting for cost, by which costs of products or services are ascertained and controlled.
Qualitative characteristics of accounting information – In order to ensure the objectivity in reporting and validity in the system, accounting information must possess certain qualitative characteristics as shown below:-
1. Reliability – Accounting information is considered to be reliable if it is free from bias and faithfully represents the facts.
2. Relevance – The information to be relevant, it must be available in time.
3. Understandability – It must be understood by those to whom it is communicated.
4. Comparability – It means that the accounting reports should be comparable with other firms to identify similarities or differences. To achieve this, the period, the format, unit of measurement etc. should be the same.

Objectives of Accounting
Role of Accounting
Accounting as an information system collects and communicates economic information about an enterprise to a wide variety of interested parties. However, accounting information relates to the past transactions and is quantitative and financial in nature, it does not provide qualitative and non-financial information. These limitations of accounting must be kept in view while making use of the accounting information.
Basic Accounting Terms
1. Entity – Entity means a reality that has a definite individual existence. Business entity means a specifically identifiable business enterprise like Super Bazaar, Jewellers, ITC Limited, etc. An accounting system is always devised for a specific business entity (also called accounting entity).
2. Transaction – The dealing of a businessman with an external party which can be expressed in monetary terms is called business transactions. In other words, all economic events in a business organization is known as transactions.
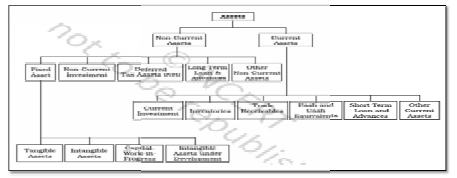
3. Assets – These are the economic resources or material things or properties of the business including the amounts due from others which can be expressed in monetary terms. It can be broadly classified into two, current assets and non-current assets.
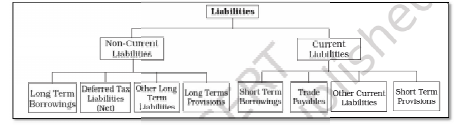
4. Liabilities – Liabilities are the obligations which an enterprise owes. It represents the amount payable by the business in future. Liabilities are classified as current and noncurrent.Eg: Creditors, Bank Loan etc.

5. Capital – It is the investment made by the owners for use in the business. It is also called owner’s equity.
6. Sales – It represents total revenue earned by a business through sale of goods or services to customers. It includes cash sales and credit sales.
7. Revenues (Income) – It represents the amount a business earns through the sale of its products or providing services to customers. It also includes earnings like interest received, dividend received, rent received, commission received, discount received etc.
8. Expenses – It represents the amount spent to earn revenue. Eg; rent, wages, salaries etc.
9. Expenditure – Spending money or incurring a liability for some benefit, service or property received is called expenditure. Purchase of goods, purchase of machinery,purchase of furniture, etc. are examples of expenditure. If the benefit of expenditure is exhausted within a year, it is treated as an expense (also called revenue expenditure).
On the other hand, the benefit of expenditure lasts for more than a year; it is treated as an asset (also called capital expenditure) such as purchase of machinery, furniture, etc.
10.Profit – It is the excess of revenue over expenses in an accounting year and represents increase in capital.
11.Gain – A profit that arises from events or transactions which are incidental to business such as sale of fixed assets, winning a court case, appreciation in the value of an asset etc.
12.Loss – It is the excess of expenses over revenue in an accounting year and represents reduction in owners’ equity or capital investment.
13.Discount – Discount is the deduction in the price of the goods sold. It may be of two types; trade discount and cash discount. Trade discount is the deduction of price at the time of selling goods, whereas cash discount means a deduction in the amount payable by a debtor within a stipulated period.
14.Voucher – The documentary evidence in support of a transaction is known as voucher.
For example, if we buy goods for cash, we get cash memo, if we buy on credit, we get an invoice; when we make a payment we get a receipt and so on.
15.Goods – It refers to commodities, products, articles or things in which a trader deals.
They refer to commodities which are purchased and are meant for resale. For stationary merchant, stationary articles like pen, pencil books etc. are his goods but for other business, it is an expense. Likewise, for a furniture dealer, furniture items like tables, chairs etc. are his goods, but for others it is an asset. They also include commodities purchased for manufacture and sale. In accounting they are called by different name, such as purchases, sales, purchases returns, sales returns and stock.
16.Drawings – It represents the amount of cash or other assets withdrawn by the owner for his personal use.
17.Purchases – It is an expense incurred for procurement of goods in a business. It includes both cash purchase and credit purchase.
18.Stock – It represents the unsold goods at the end of accounting year. It includes unsold goods, raw materials, semi finished goods etc. Stock is also called inventory.
Inventory at the end of the accounting year is called closing stock, while the same at the beginning of the year is called opening stock.
19.Debtors / Accounts receivable – A debtor is a person who owes money to the business as he has received some benefit from the business. The amounts due from different persons are totaled on the close of the accounting period and are shown under the heading Sundry Debtors or Accounts Receivable on the asset side of the balance sheet.
20.Creditors / Accounts payable – A creditor is a person to whom the business owes money as he has given some benefit to the business. The amounts due to various persons are totaled on the close of the accounting period and are shown under the head Sundry Creditors or Accounts Payable on the liability side of the balance sheet.
Important Questions Introduction to Accounting Class 11 Accountancy
Question: Distinguish between debtors and creditors ; profit and gain.
Answer: The following are the differences between debtors and creditors
| Debtors | Creditors |
| Debtors are the persons and/or other entities who owe to an enterprise certain amount for buying goods and services on credit | Creditors are the persons and/or other entities to whom the an enterprise has to pay an amount after purchasing the goods and service on credit. |
| The total amount standing against the debtors on closing date is recorded in the balance sheet as sundry creditors on the assets side. | The total amount standing to the favour of creditors on the closing date is recorded in the balance sheet as sundry creditors on the liabilities side |
| To encourage the debtors to pay the amount within stipulated period, a cash discount is offered to them as incentive. | To receive the payments on time, the creditors offer cash discount incentives. |
| Profit | Loss |
| Profit represents the excess of revenue of a period over expenses, during an accounting year. | Loss represents the excess of expenses of a period over revenue/income, during an accounting year. |
| Profit increases the owner’s equity | Loss decreases the owner’s equity |
| Events or transactions which are incidental to business such as sale of fixed assets, winning a court case, appreciation in the value of an asset will result in profit. | Events or transactions which are incidental to business such as loss of value without receiving any benefit in return (due to theft or fire accident), loss on sale of fixed assets result in a loss. |
Question: Describe the role of accounting in the modern world.
Answer: Language of a business: The accounting process describes and analyzes huge amount of data belonging to an enterprise by
● measuring
● classifying
● and summarizing
It also presents this information in the form of reports and statements. This information helps the users to gauge the financial condition and results of
operation of a business. Thus accounting plays the role of the language of business.
2. Historical record: Accounting provides a detailed overview of the past transactions and serves to maintain historical recording of the information.
This helps the users to make intra-period comparison and evaluate how the business is doing. It also serve as a valid proof in case of any conflicts arising.
3. Current economic reality: It provides reliable and relevant financial information about the current position of the business. Various users thus rely on this information and use it as a guideline to set their strategy towards the business.
4. Information System: Being the information system it collects and communicates economic information about the enterprise to various users.
The information provided is both relevant and reliable. Thus the users rely on this information system to change their strategies towards the business.
5. Service to Users: Accounting makes it easy for the users to understand, compare and judge the business by presenting the information in the relevant and reliable manner. The users rely on this information to make various decisions and plan and in many other ways. This it performs the service
activity to the users.
Question: Explain the meaning of gain and profit. Distinguish between these two terms.
Answer: Gain: Gain is the profit that results from the events or transactions that are incidental to business such as the sale of fixed assets, winning a court case,
appreciation in the value of an asset.
Profit: Profit is the excess of revenues of a period over its related expenses during an accounting year. Profit increases the investment of the owner.
| Gain | Profit |
| Gain arises from the events or transactions which are incidental to business. | Profit is the excess of revenues of a period over its related expenses during an accounting year. |
| The transactions that yield the gain are not part of the core business. | The transactions that yield the profit are part of the core business. |
| Gain is not repetitive in nature. | Profit arises as the number of products sold increases. The more the number of products sold or the lesser the expenses, the more is the profit. |
| Examples include sale of fixed assets, winning a court case, appreciation in the value of an asset. | Excess of income after deducting the expenses. |
Question: “The role of accounting has changed over the period of time” – Do you agree? Explain.
Answer: I agree with the fact that the role of accounting had changed over a period of time.
Especially the advancements in economic development greatly contributed to changing the role of accounting and its scope at a broader level.
● Initially accounting was looked upon as the art of recording, classifying and summarizing in
a. significant manner
b. in terms of money
c. transactions and events
which are at-least partially financial in nature and interpreting the results thereof.
● Then accounting became the process of
a. identifying
b. measuring
c. communicating
economic information to allow informed judgments and decisions by users of information.
● And then accounting assumed the role of providing quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities that is intended to be
useful in making economic decisions.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: State what is the end product of financial accounting.
Answer: The end product of financial accounting is
● Income statement: The income statement includes the trading and/or profit and loss account. It ascertains the financial results of any business in terms of gross (or net) profit or loss.
● Balance Sheet: Balance sheet provides the true financial position of a business. It presents the information in terms of assets and liabilities of a business unit to the users.
Question: Who are the external users of information?
Answer: External users of information are the users who are not part of the business but are interested in the accounting information. They include:
1. Creditors: Banks and other financial institutions, debenture holders and other lenders.
2. Customers
3. Labour Unions
4. Regulatory Agencies: Department of Company Affairs, Registrar of Companies, Securities Exchange Board of India
5. Shareholders: present and potential investors.
6. Trade Associations
7. Tax authorities
Question: Who are the users of accounting information?
Answer: The following are the users of accounting information.
a. Internal users: Chief Executive, Financial Officer, Vice President, Business Unit Managers, Plant Managers, Store Managers, Line Supervisors etc
b. External users: Shareholders, creditors, Tax authorities, regulatory agencies, labour unions, trade associations, stock exchange and customers.
Question: Define accounting.
Answer: Accounting is the process of
● identifying
● measuring
● recording
● and communicating
the required information related to the economic events of an organization, to the interested users of this information.
Question: Enumerate main objectives of accounting.
Answer:The main objectives of accounting are:
1. Maintenance of Records of Business Transactions.
2. Calculation of Profit and Loss
3. Depiction of financial position.
4. Providing accounting information to the users interested in the information.
Question: ‘Accounting information should be comparable’. Do you agree with this statement. Give two reasons.
Answer: Accounting information should be comparable due to the following reasons. Lack of comparability will make these aspects erroneous/difficult.
● It enables the interested uses to assess how a firm is performing as compared to other entities.
It also helps in assessing how a firm has performed during different periods by comparing the financial reports of different periods.
Question: State the nature of accounting information required by long-term lenders.
Answer:The long-term lenders seek the following accounting information
● Liquidity
● Operational Efficiency
● Potential growth prospects
● Profitability
● Repaying capacity of the business.
Question: Enumerate information needs of management.
Answer: The management needs the following information which helps in:
1. Budgeting
2. Business planning
3. Capital Expenditure decisions
4. Decision making
5. Pricing decisions
6. Profitability assessment
Question: Give any three examples of revenues.
Answer:The following are few examples of revenue.
● Commission
● Dividends
● Royalties
● Rent Received
Question: If the accounting information is not clearly presented, which of the qualitative characteristic of the accounting information is violated?
Answer: The lack of clear presentation will result in the violation of the qualitative characteristics namely
● Reliability: The data will be erroneous/biased and loses faithfulness.
● Relevance: The information loses the validity
● Understandability: It will be difficult to understand and is prone to errors.
● Comparability: Comparison with other reports will be difficult/erroneous resulting in biased interpretations.
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Question: What do you mean by an asset and what are different types of assets?
Answer: Assets are the economic resources of an enterprise which can be expressed in monetary terms. In other words assets are items that have monetary value and are used by the business in its day to day operations. Assets shown on the asset side of the balance sheets. Assets are broadly classified into two types.
1. Fixed Assets: Fixed assets are the assets that are held on a long-term basis.
They are used for the normal operations of the business. Examples includes
● Land
● Buildings
● Furniture
● Fixtures
● Plant
● Machinery
2. Current Assets: Current assets are the assets that are held on a short-term
basis. Examples are :
● Bank Balances
● Bills Receivable (notes receivable)
● Cash balances
● Debtors (accounts receivable)
● Stock (inventory)
● Temporary marketable securities
Question: Giving examples, explain each of the following accounting terms:
● Fixed assets
● Revenue
● Expenses
● Short-term liability
● Capital
Answer: Fixed Assets: Fixed assets are the assets held on a long-term basis for the normal
operations of the business. Examples
● Land
● Buildings
● Furniture
● Fixtures
● Plant
● Machinery
Revenue: Revenue, also called as income, is the amount that the business has earned through its normal business activities by selling its products and/or providing services to the customers.
Examples are:
● Commission
● Dividends
● Royalties
● Rent Received
Expenses: The cost incurred by the business during the process of earning revenue is called as expenses. Usually, the expenses are measured by the cost of assets consumed or services used during an accounting period.
Examples are:
● Cost of heater, light, water, telephone
● Depreciation
● Rent
● Salaries
● Wages
Short-term liabilities: Short term liabilities are those liabilities that are payable
within a period of one year.
Examples are:
● bank Overdraft
● Bills Payable
● Creditors
Capital: Capital is the amount invested by the owner in the business. The capital may be invested in the form of cash or assets. The capital is an obligation and is a claim on the assets of the business (the owner can claim this later on). It is recorded on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
Examples are:
a. Buildings
b. Land
c. Cash
d. Machinery
e. Equipment
Question: Define revenues and expenses?
Answer: Revenues: Revenue, also called as income, is the amount that the business has earned through its normal business activities by selling its products and/or providing services to the customers.
Examples are:
● Commission
● Dividends
● Royalties
● Rent Received
Expenses: The cost incurred by the business during the process of earning revenue is called as expenses. Usually, the expenses are measured by the cost of assets consumed or services used during an accounting period.
Examples are:
● Cost of heater, light, water, telephone
● Depreciation
● Rent
● Salaries
● Wages
Question: Explain the qualitative characteristics of accounting information.
Answer: The following are the qualitative characteristics of accounting information. The are the attributes of the accounting information that improve the understand-ability and usefulness.
a. Reliability: The information becomes reliable when the users are able rely on it. It is determined by the degree of correspondence between what the information conveys about the transactions or events that have
● occurred
● measured
● and displayed
To be more reliable, the information must be
● credible
● verifiable by independent parties
● use the same method of measuring
● be neutral and faithful.
b. Relevance: The information is relevant, when it is
● available on time
● helpful in prediction and feedback
● influence the decisions of the users When it meets the above requirements, it will
● help the users to predict about the outcome of past, present and future events.
● confirming or correcting their past evaluations.
c. Understand-ability: The information is said to be understandable when the users/decision-makers will interpret it in the same sense as the ones who have prepared it. In other-words it should not have any communication gap. Thus the understand-ability necessitates that the accountants should present the
comparable information in the most intelligible manner without sacrificing relevance and reliability.
d. Comparability: The information apart from being relevant and reliable at a particular time, in a particular circumstance or for a particular reporting entity, should also enable the general users to compare various aspects of an entity with those of other entities over different periods of time. When the
accounting reports
● belong to a common period
● use common unit of measurement
● use common format of reporting they can be easily compared.
Question: What is accounting? Define its objectives.
Answer: Accounting: Accounting is the process of
● identifying
● measuring
● recording
● and communicating
the required information related to the economic events of an organization, to the interested users of this information.
The following are the objectives of accounting:
a. Maintenance of records of business transactions: As it is beyond the control of humans to remember the various transactions taking place in the business, accounting is used for systematic maintenance of all the financial transactions in books of accounts. Apart from storing the data, it serves as an
evidence and allows verification when required.
b. Calculation of profit and loss: To provide profit and loss account prepared by considering the various incomes and expenses. This information gives the the net results of the business to the owners, periodically. This helps them to know whether the business is running with profits or not.
c. Depiction of financial position: Provide the balance sheet by considering the assets owned and liabilities owed. This gives the financial position of the business.
d. Providing accounting information to its users: After accounting information is generated by the accounting process, it is communicated to the interested users namely internal users and external users to serve them as the basis in various decision making processes, planning controlling.
Question: Explain the factors which necessitated systematic accounting.
Answer: The following are the factors that have led to systematic accounting.
a. Recording only those transactions which are financial in nature: Among all the transactions and events that occur in the organization, only those transactions which are financial in nature are recorded.
Non-financial events like hiring, promotion, holding conferences etc are not recorded.
b. Recording the transactions always in the monetary terms: Each of the economic events are recorded in terms of currency. For instance, furniture is recorded as worth Rs.75,000. In other-words the recorded information is always expressed in monetary units.
c. Recording the information: The recording of information is an art. The information should be carefully and accurately segregated keeping the recording rules under consideration. In addition the economic events are recorded in chronological order. In small to medium firm accountants
maintain journals for this purpose. As the size of the firm increases, it might be necessary to further segregate the journal into subsidiary records.
d. Classification: The economic transactions from the journals/subsidiary records are then skillfully classified and recorded into the respective account records namely ledgers.
e. Summation: The summarized business transactions take the form of trading account, profit and loss account, balance sheet and traial balance depending on the intended users for whom these accounts are prepared.
f. Analyzing and interpreting the data: When accounting records are prepared using this systematic procedure, it helps the users to analyze and interpret the accounting information efficiently and accurately. When presented in various formats like charts, graphs, accounting statements,
report it becomes easier to communicate it to the users and also it improves the understand-ability and comparability. The users use this information for controlling, decision making and planning
Question: What is the primary reason for the business students and others to familiarize themselves with the accounting discipline?
Answer:The students of business studies and entrepreneurship familiarize themselves with the accounting principles as accounting is the language of the business. It also help them to
● understand the various principles of accounting
● maintain records of business information
● summarize accounting information and there by understand the financial position of the business
● accurately interpret the accounting information.
Question: Describe the informational needs of external users.
Answer: The following are the various needs of external users.
a. Customers: Customers need the information to ensure the continuity of the business so that they have good probability of supply of products, parts and after sales service.
b. Competitors: Competitors need the information on the relative strengths and weaknesses of their competition and for comparative and bench-marking purposes. Their information need is strategic in nature.
c. Government and other regulatory agencies: They need information to decide about the allocation of resources and to ensure that the business is complying with the regulations.
d. Investors and potential investors: They need information to assess the risks and the return on their investment.
e. Lenders and financial institutions: Information on the creditworthiness of the business and its ability to repay loans.
f. Social responsibility groups: They need information to assess the impact on environment and its protection.
g. Unions and employee groups: They need this information to understand the stability, profitability and distribution of wealth within the business.






